Introduction & Background
Baldness, also known as alopecia, refers to the loss or absence of hair on the scalp or other parts of the body. While some degree of hair thinning is a natural part of aging, baldness can significantly affect self-esteem and confidence. It may be temporary or permanent, depending on the cause. Both men and women are affected, though the patterns and reasons may differ.
Causes of Baldness
- Genetics (Androgenetic Alopecia) – The most common cause, often referred to as male or female pattern baldness.
- Hormonal Imbalances – Conditions like thyroid disorders, pregnancy, menopause, and PCOS can trigger hair loss.
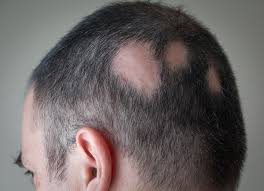
- Medical Conditions – Autoimmune diseases like alopecia areata, lupus, diabetes.
- Medications – Chemotherapy, antidepressants, blood thinners, and high blood pressure drugs.
- Nutritional Deficiencies – Lack of protein, iron, biotin, zinc, and vitamin D.
- Physical or Emotional Stress – Can push hair follicles into a resting phase (telogen effluvium).
- Infections – Fungal infections like ringworm can cause bald patches.
- Hair Treatments & Styling – Excessive bleaching, straightening, and tight hairstyles (traction alopecia).
- Radiation Therapy – Often results in localized hair loss.
- Aging – Natural hair follicle shrinkage over time.
Indications of Baldness
- Noticeable thinning on the top of the head
- Receding hairline, especially in men
- Circular or patchy bald spots
- Sudden loosening of hair
- Full-body hair loss (often due to medical treatment)
- Scaling or redness in areas of hair loss
Symptoms of Baldness
- Gradual thinning of hair
- Hair falling out in clumps
- Scalp becoming more visible
- Bald patches appearing suddenly
- Itching or burning sensation (in some conditions)
Prevention Strategies of Baldness
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals
- Avoid excessive heat styling or chemical treatments
- Manage stress through yoga, meditation, or counseling
- Treat underlying medical conditions early
- Avoid tight hairstyles that pull on the scalp
- Use mild shampoos and conditioners suited to your hair type
- Avoid smoking and reduce alcohol consumption
- Regular scalp massages to improve blood circulation
Myths and Facts About Baldness
- Myth: Baldness comes only from the mother’s side.
Fact: Genetics from both parents play a role. - Myth: Wearing hats causes baldness.
Fact: Hats do not affect hair growth unless excessively tight. - Myth: Frequent washing leads to hair loss.
Fact: Washing keeps the scalp clean and doesn’t cause hair loss. - Myth: Hair loss is always permanent.
Fact: Many types of baldness are reversible with treatment.
Treatments and Therapy
Medication-Based Treatments
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): Over-the-counter topical solution
- Finasteride (Propecia): Prescription pill for men
- Spironolactone: Used in women with hormonal hair loss
Surgical Treatments
- Hair Transplant Surgery: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) or Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
- Scalp Reduction or Flap Surgery
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Stimulates hair growth
- Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP): Cosmetic solution for visual density
Lifestyle and Behavioral Interventions
- Healthy diet
- Regular exercise
- Stress reduction techniques
Alternative and Complementary Medicine
- Ayurvedic oils and massages
- Herbal supplements (consult doctor first)
- Acupuncture (limited evidence)
Psychotherapy and Counseling
- Helps manage emotional distress due to appearance changes
- Addresses body image and self-esteem
Immunizations and Vaccines
- No direct vaccines for baldness, but keeping up with health protects scalp health indirectly
Stem Cell Therapy
- Emerging treatment still under research
- Involves regenerating hair follicles from stem cells
Gene Therapy
- Promising area but not widely available
- Targets specific genes involved in hair loss
Top 20 FAQs on Baldness
- What is the most common cause of baldness?
Genetic predisposition (androgenetic alopecia). - Can baldness be reversed?
In many cases, yes, especially if caught early. - Does stress cause hair loss?
Yes, especially in telogen effluvium. - Are there side effects to Minoxidil or Finasteride?
Yes, they include scalp irritation or decreased libido. - Can women go bald too?
Yes, usually as diffuse thinning rather than patches. - Is hair transplant permanent?
Generally, yes, but depends on technique and care. - What vitamin is best for hair loss?
Biotin, Vitamin D, and Iron are important. - Can a poor diet cause baldness?
Absolutely. Nutritional deficiencies are a major factor. - Does wearing a hat cause baldness?
No, it’s a myth. - How long before hair grows back after loss?
Usually 3–6 months, depending on the cause. - Does DHT cause baldness?
Yes, DHT sensitivity affects hair follicles. - Is laser therapy effective for hair loss?
It can be helpful, though results vary. - Can shampoos regrow hair?
They can support scalp health, not regrow hair alone. - Is baldness related to testosterone levels?
It’s more about DHT sensitivity than testosterone itself. - Does smoking cause hair loss?
Yes, it impairs blood flow to hair follicles. - What is traction alopecia?
Hair loss from tight hairstyles or pulling. - Are natural oils like castor oil helpful?
They may help with scalp condition but evidence for regrowth is limited. - Can pregnancy cause hair loss?
Yes, post-partum hair loss is common. - Is alopecia areata curable?
No cure, but treatments can help regrow hair. - When should I see a doctor for hair loss?
If you notice sudden, patchy, or excessive loss.
Conclusion
Baldness is a common condition with various causes ranging from genetics to lifestyle and medical factors. While it can be distressing, advancements in medicine offer a wide range of treatments—from topical solutions to transplants and even gene therapy. Early detection, a healthy lifestyle, and professional guidance can go a long way in managing hair loss and improving hair health.