Introduction & Background
Gynecomastia refers to the condition of enlarged male breast tissue, which can occur in one or both breasts. It is a common condition that affects men of all ages, though it is most prevalent during adolescence and in older men. The word “gynecomastia” originates from Greek, meaning “woman-like breasts” (gyne = woman, mastos = breast).
In most cases, gynecomastia is benign and does not pose any significant health risks. However, it can cause emotional distress and self-esteem issues for affected individuals due to the physical appearance. The condition can be caused by an imbalance of hormones, specifically an increase in estrogen levels or a decrease in testosterone.
Treatment for gynecomastia typically involves addressing the underlying causes, medications, or in severe cases, surgical intervention.
Causes of Gynecomastia
Several factors can contribute to the development of gynecomastia, which may be linked to hormone imbalances, medications, and lifestyle choices. Common causes include:
- Hormonal Imbalance:
- Estrogen and Testosterone Levels: The main cause of gynecomastia is an imbalance between estrogen and testosterone levels. Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, helps inhibit breast tissue growth, while estrogen promotes it. When estrogen levels become too high or testosterone levels too low, breast tissue enlargement occurs.
- Adolescence:
- During puberty, many boys experience temporary gynecomastia due to hormonal changes as the body undergoes rapid growth and development. In most cases, this condition resolves on its own without the need for intervention.
- Aging:
- As men age, their testosterone levels naturally decrease, which can lead to an increased proportion of estrogen. This often results in the development of gynecomastia in older men, typically around the age of 50 or older.
- Medications:
- Certain medications can cause gynecomastia as a side effect, such as anti-androgens (used to treat prostate enlargement), anabolic steroids, certain antidepressants, and medications for heart conditions.
- Health Conditions:
- Medical conditions that affect hormone levels can also contribute to gynecomastia. Conditions like liver disease, kidney failure, thyroid disorders, and obesity (due to increased estrogen production in fat tissue) may increase the likelihood of gynecomastia.
- Substance Use:
- The use of substances such as alcohol, marijuana, heroin, and certain drugs can lead to hormonal changes that promote gynecomastia.
- Genetic Factors:
- In some cases, gynecomastia may be hereditary, passed down from parents to offspring through genetic predisposition.
Indications of Gynecomastia
The primary indication for gynecomastia is the visible enlargement of breast tissue in men. It is important to note that gynecomastia should not be confused with pseudogynecomastia, which involves fat accumulation rather than true glandular tissue growth.
Other indications include:
- Pain or Tenderness: In some cases, gynecomastia may cause pain, soreness, or tenderness in the breast tissue.
- Discomfort or Self-Consciousness: Many individuals with gynecomastia report feeling self-conscious, especially in situations that involve removing shirts, such as at the beach or in a gym setting.
- Visible Changes in Breast Shape: The enlargement of the breast may be unilateral (only one side) or bilateral (both sides). The breast may appear more prominent or have a lump or swelling under the nipple.
Symptoms of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia presents with several noticeable symptoms that can help in identifying the condition:
- Enlarged Breast Tissue: The most significant symptom is the presence of firm, glandular tissue in the breast area.
- Swelling or Tenderness: The affected breast may feel tender to the touch or swollen, particularly around the areola (the dark area around the nipple).
- Nipple Discharge: In some cases, gynecomastia may cause a milky discharge from the nipples, although this is rare in men.
- Asymmetry: The breasts may appear uneven in size, and one side may be more prominent than the other.
Prevention Strategies for Gynecomastia
While it may not always be possible to prevent gynecomastia, some steps can be taken to reduce the risk:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is a contributing factor to gynecomastia, as excess fat can lead to higher estrogen levels. Maintaining a healthy weight through proper diet and exercise can help.
- Avoid Drugs and Alcohol: Limiting or avoiding substances like alcohol, marijuana, anabolic steroids, and certain medications that can interfere with hormone levels can prevent the onset of gynecomastia.
- Monitor Hormonal Health: Regular checkups to monitor testosterone levels can help identify any imbalances early.
- Limit Exposure to Endocrine Disruptors: Certain chemicals in food, personal care products, and the environment can disrupt hormone balance. Minimizing exposure to these substances may reduce the risk of developing gynecomastia.
Myths and Facts About Gynecomastia
Myth 1: Gynecomastia only happens to overweight men.
- Fact: While obesity can contribute to gynecomastia, even lean men can develop the condition if there is an imbalance in their hormone levels.
Myth 2: Gynecomastia is caused by a lack of exercise.
- Fact: Gynecomastia is not solely caused by inactivity. Hormonal imbalances, medications, and genetics are much more significant factors.
Myth 3: Gynecomastia always requires surgery.
- Fact: Many cases of gynecomastia resolve on their own without surgical intervention, especially in adolescents. Medical treatments or lifestyle changes may also be effective in some cases.
Treatments and Therapy
Medication-Based Treatments
- Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs): Medications like tamoxifen are sometimes used to treat gynecomastia by blocking estrogen receptors and reducing breast tissue growth.
- Aromatase Inhibitors: These medications reduce the conversion of androgens (such as testosterone) to estrogen, potentially helping to balance hormone levels.
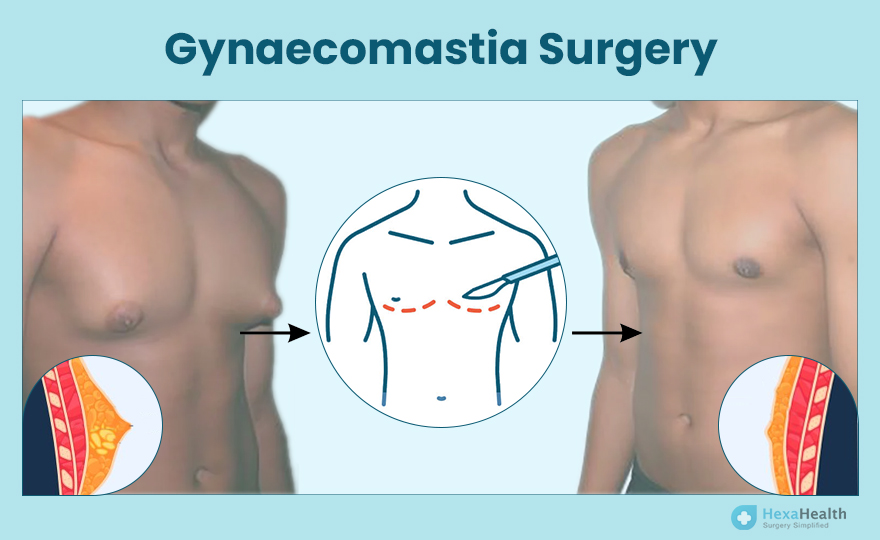
Surgical Treatments
When medication fails or the condition is severe, surgical treatment may be recommended. The most common surgical procedure for gynecomastia is:
- Liposuction: This technique involves the removal of excess fatty tissue in the chest area, which can help reduce the size of the breasts.
- Mastectomy: In more severe cases, a surgical procedure called mastectomy may be performed to remove the glandular tissue from the breast.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Although physical therapy does not directly treat gynecomastia, it may help reduce discomfort, especially if the condition has caused muscular tension around the chest.
Lifestyle and Behavioral Interventions
- Diet and Exercise: Following a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity, especially strength training, can help maintain overall health and reduce excess fat.
- Stress Management: Reducing stress can help prevent hormonal imbalances caused by increased levels of cortisol.
Alternative and Complementary Medicine
Some alternative treatments like herbal supplements (e.g., saw palmetto or flaxseed) claim to balance hormones, but their effectiveness is largely unproven, and they should be used cautiously under a doctor’s supervision.
Psychotherapy and Counseling
For individuals who experience psychological distress due to the condition, counseling and therapy may be beneficial. A therapist can help individuals with self-esteem issues and body image concerns.
Immunizations and Vaccines
There are no specific vaccines or immunizations for gynecomastia, as it is not an infectious condition. However, maintaining overall health through immunizations may help reduce the risk of underlying health conditions that could contribute to gynecomastia.
Stem Cell Therapy and Gene Therapy
Both stem cell therapy and gene therapy are in early stages of research for a variety of conditions, including gynecomastia. These therapies may have potential in the future but are not yet proven or widely available.
Top 20 FAQs on Gynecomastia
- What is gynecomastia?
- Answer: Gynecomastia is a condition where men develop enlarged breast tissue due to an imbalance between estrogen and testosterone. It can occur in one or both breasts.
- How can I tell if I have gynecomastia?
- Answer: You may notice enlarged, firm breast tissue under the nipple, and in some cases, it can be tender or swollen. If you’re unsure, it’s best to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis.
- What causes gynecomastia?
- Answer: Gynecomastia can be caused by hormonal imbalances (higher estrogen or lower testosterone), medications, substance use (like alcohol or steroids), obesity, or certain health conditions such as liver disease or kidney failure.
- Can gynecomastia go away on its own?
- Answer: In some cases, especially during adolescence, gynecomastia may resolve on its own. However, if it persists or causes distress, medical intervention may be necessary.
- When should I seek medical treatment for gynecomastia?
- Answer: You should seek medical treatment if the condition causes significant pain, emotional distress, or if it does not resolve on its own within a few months.
- Is gynecomastia common in teenagers?
- Answer: Yes, gynecomastia is quite common during adolescence due to hormonal changes as the body matures. It often resolves without treatment as puberty progresses.
- How is gynecomastia diagnosed?
- Answer: A doctor diagnoses gynecomastia through a physical examination, medical history, and sometimes imaging tests like an ultrasound or mammogram to rule out other conditions.
- Does gynecomastia affect both breasts?
- Answer: Gynecomastia can affect one or both breasts. In some cases, one side may be more prominent than the other.
- Can exercise help reduce gynecomastia?
- Answer: Exercise, particularly strength training, can help reduce excess fat in the chest area, but it will not address the glandular tissue that causes true gynecomastia.
- What medications can treat gynecomastia?
- Answer: Medications such as Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs) like tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors can sometimes be used to treat gynecomastia, especially in cases related to hormonal imbalance.
- Can gynecomastia be treated without surgery?
- Answer: Yes, gynecomastia can be treated without surgery through medications, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, weight management. However, surgery is often required for more severe cases.
- Is surgery the best treatment for gynecomastia?
- Answer: Surgery, like liposuction or mastectomy, may be the best treatment for persistent or severe gynecomastia that does not improve with other treatments.
- What is the recovery time after gynecomastia surgery?
- Answer: Recovery time after gynecomastia surgery typically ranges from a few days to a few weeks, depending on the procedure. Full recovery and final results may take several months.
- Are there risks associated with gynecomastia surgery?
- Answer: As with any surgery, there are risks including infection, scarring, changes in nipple sensation, and uneven results. It’s important to discuss these risks with your surgeon beforehand.
- How much does gynecomastia surgery cost?
- Answer: The cost of gynecomastia surgery varies based on location, the surgeon’s experience, and the complexity of the procedure. On average, it can range from $3,000 to $8,000 or more.
- Can gynecomastia affect my fertility?
- Answer: Gynecomastia itself does not directly affect fertility, but the hormonal imbalances that cause it (like low testosterone) may have an impact on reproductive health. Consult a doctor if you’re concerned about fertility.
- Is gynecomastia linked to breast cancer?
- Answer: Gynecomastia is not typically linked to breast cancer. However, in rare cases, enlarged breast tissue may mask a more serious condition, so it’s important to have it evaluated by a doctor.
- Can smoking or alcohol cause gynecomastia?
- Answer: Yes, smoking and alcohol use can contribute to the development of gynecomastia by affecting hormone levels. Alcohol, in particular, can raise estrogen levels in men.
- How can I prevent gynecomastia from returning after surgery?
- Answer: To prevent recurrence, maintain a healthy weight, avoid drugs and substances that disrupt hormones, and follow the doctor’s post-operative care instructions carefully.
- Is gynecomastia curable?
- Answer: Gynecomastia can be effectively treated, especially with surgery or medication. While it may not always be “cured” in the traditional sense, treatment options can significantly improve the condition.
Conclusion
Gynecomastia is a common but often misunderstood condition. While it can cause emotional and psychological distress, there are several effective treatment options, including lifestyle changes, medications, and surgical procedures. Early intervention and proper management can help improve both physical appearance and quality of life for those affected by this condition. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments available for gynecomastia empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being.