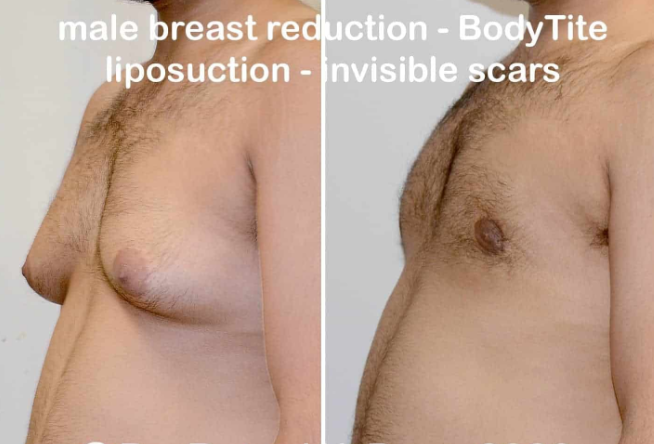
Introduction & Background
Male breast reduction is a medical procedure aimed at reducing the size of enlarged male breasts, a condition known as gynecomastia. Gynecomastia is characterized by the abnormal development of glandular tissue in the male chest, which can result in a more feminine appearance of the breasts. This condition can affect men of all ages and can be a source of psychological distress, especially in adolescence or adulthood. The condition can be mild or severe, with some cases causing significant cosmetic and emotional issues.
Breast reduction surgery for males aims to remove excess fat, glandular tissue, and skin to restore a more masculine contour to the chest. Male breast reduction can significantly improve self-esteem and quality of life, offering both physical and psychological benefits.
Causes of Gynecomastia
The causes of gynecomastia can be classified into physiological, pathological, and medication-induced categories. Some of the main causes include:
- Hormonal Imbalances:
- The most common cause of gynecomastia is an imbalance between estrogen (female hormone) and testosterone (male hormone). Increased levels of estrogen or reduced testosterone levels can stimulate breast tissue growth.
- Adolescence:
- During puberty, boys may experience a temporary increase in breast size due to hormonal changes. In most cases, this condition resolves on its own over time.
- Aging:
- As men age, their testosterone levels naturally decrease, which can lead to a relative increase in estrogen levels, contributing to the development of gynecomastia.
- Obesity:
- Excess fat in the chest area can mimic the appearance of gynecomastia. While it is not true gynecomastia (glandular tissue growth), this fat accumulation can give the chest a feminine look.
- Medications:
- Certain medications can lead to the development of gynecomastia as a side effect. These include drugs used for cancer treatment (chemotherapy), heart conditions, antidepressants, and anabolic steroids.
- Health Conditions:
- Conditions such as liver disease, kidney failure, hyperthyroidism, and pituitary tumors can also cause hormonal imbalances leading to gynecomastia.
- Substance Abuse:
- Alcohol, marijuana, and heroin use has been linked to gynecomastia due to their effects on hormone levels and liver function.
Indications of Male Breast Reduction
Male breast reduction surgery is typically recommended for individuals who meet the following criteria:
- Persistent Gynecomastia:
- Men whose gynecomastia has persisted for a significant period, typically more than a year, and has not improved with conservative treatments.
- Psychological Distress:
- Men who experience emotional discomfort, low self-esteem, or embarrassment due to the appearance of their breasts. This may affect their social interactions or body image.
- Physical Discomfort:
- Some men experience physical symptoms, such as tenderness, pain, or nipple sensitivity due to enlarged breast tissue.
- Non-Responsive to Other Treatments:
- When lifestyle changes (such as weight loss or hormonal therapy) fail to reduce the size of the breasts.
- Stable Health:
- Ideal candidates should be in generally good health, free from conditions that could complicate surgery, such as heart disease or diabetes.
Symptoms of Gynecomastia
The primary symptom of gynecomastia is the enlargement of one or both breasts in men. Additional symptoms may include:
- Tenderness or Sensitivity:
- The breast tissue may feel tender or sensitive to touch.
- Nipple Discharge:
- In rare cases, a milky discharge from one or both nipples can occur.
- Uneven Breast Development:
- The condition may affect one or both breasts unevenly, leading to asymmetry.
- Self-Consciousness:
- Many individuals with gynecomastia feel self-conscious about their chest appearance, especially in social or intimate settings.
Prevention Strategies for Gynecomastia
While some causes of gynecomastia, like hormonal fluctuations during puberty or aging, cannot be avoided, there are steps men can take to minimize their risk:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Obesity is a significant risk factor for gynecomastia. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can reduce the likelihood of developing enlarged breasts.
- Avoid Substance Abuse:
- Reducing or eliminating the use of drugs such as anabolic steroids, marijuana, and alcohol can lower the risk of gynecomastia.
- Monitor Medications:
- Be aware of medications that can cause gynecomastia, and discuss alternatives with a healthcare provider if necessary.
- Regular Health Check-ups:
- Regular visits to a healthcare provider can help identify and address underlying health conditions that may contribute to gynecomastia.
Myths and Facts About Gynecomastia
- Myth: Gynecomastia is the same as “man boobs” (pseudo-gynecomastia).
- Fact: Gynecomastia involves the growth of glandular tissue, while “man boobs” (pseudo-gynecomastia) are caused by excess fat. They may look similar, but the underlying causes are different.
- Myth: Gynecomastia only occurs in overweight men.
- Fact: While obesity can contribute to gynecomastia, it can also affect men with normal weight due to hormonal imbalances or other causes.
- Myth: Gynecomastia can be treated with exercises alone.
- Fact: Exercise can help reduce fat in the chest area, but it cannot address the glandular tissue responsible for true gynecomastia. Surgery may be necessary.
- Myth: Surgery for gynecomastia is only for cosmetic purposes.
- Fact: In addition to improving appearance, surgery can also alleviate physical discomfort and psychological distress associated with the condition.
Treatments and Therapy for Gynecomastia
Medication-Based Treatments
- Hormonal Therapy:
- In cases where gynecomastia is caused by hormonal imbalances, medications such as anti-estrogens (e.g., tamoxifen) or aromatase inhibitors can be prescribed to reduce the effects of estrogen and restore balance.
- Discontinuation of Medications:
- If gynecomastia is caused by a medication, discontinuing or changing the medication may help resolve the condition.
Surgical Treatments
- Liposuction:
- For cases where gynecomastia is primarily caused by excess fat, liposuction can be used to remove fat from the chest area.
- Mastectomy (Tissue Removal):
- If glandular tissue is the primary cause of gynecomastia, a mastectomy procedure may be necessary. This involves the surgical removal of the excess glandular tissue through small incisions.
- Combination Surgery:
- In many cases, a combination of liposuction and mastectomy may be recommended for optimal results.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Post-surgery, physical therapy may be recommended to ensure that the chest heals properly and to regain strength and flexibility. Rehabilitation can also help address any scarring and improve overall chest appearance.
Lifestyle and Behavioral Interventions
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help maintain the results of male breast reduction surgery:
- Diet and Exercise:
- Maintaining a balanced diet and regular exercise routine helps prevent weight gain, which could re-trigger the development of gynecomastia.
- Avoiding Drug Use:
- Steer clear of substances like anabolic steroids and alcohol to prevent future occurrences of gynecomastia.
Alternative and Complementary Medicine
While not widely supported by clinical research, some men turn to herbal supplements or homeopathic remedies. However, their effectiveness remains uncertain, and they should be discussed with a healthcare provider before use.
Psychotherapy and Counseling
For men suffering from emotional distress due to gynecomastia, counseling or therapy may be beneficial. Addressing body image concerns can help improve self-esteem and reduce anxiety.
Immunizations and Vaccines
There are no specific vaccines or immunizations for gynecomastia.
Stem Cell Therapy
Research into the use of stem cells for tissue regeneration and repair is ongoing, but it is not yet a proven or widely available treatment for gynecomastia.
Gene Therapy
Gene therapy is a promising field in the treatment of many conditions, but as of now, it is not a standard treatment for gynecomastia.
Top 20 FAQ on Male Breast Reduction
- What is gynecomastia?
- What causes gynecomastia?
- How do I know if I need male breast reduction surgery?
- What are the risks of male breast reduction surgery?
- Is gynecomastia reversible without surgery?
- How long does male breast reduction surgery take?
- Will the surgery leave scars?
- How long is the recovery period after surgery?
- Are there any non-surgical treatments for gynecomastia?
- How much does male breast reduction surgery cost?
- Is gynecomastia dangerous?
- Will my insurance cover male breast reduction surgery?
- Can exercise reduce gynecomastia?
- Can gynecomastia return after surgery?
- Are there age restrictions for male breast reduction surgery?
- What are the psychological effects of gynecomastia?
- Can male breast reduction be done under local anesthesia?
- How can I find a good surgeon for gynecomastia?
- What happens during the consultation for male breast reduction?
- Can gynecomastia be prevented?
Conclusion
Male breast reduction is an effective procedure for addressing gynecomastia, a condition that can affect men of all ages. The surgery offers both physical and emotional benefits, improving chest appearance and self-esteem. Although non-surgical treatments may work for some, surgery remains the most reliable option for persistent or severe gynecomastia. With proper care, patients can expect positive results and an improved quality of life.