Introduction to Dilation And Curettage (D & C)
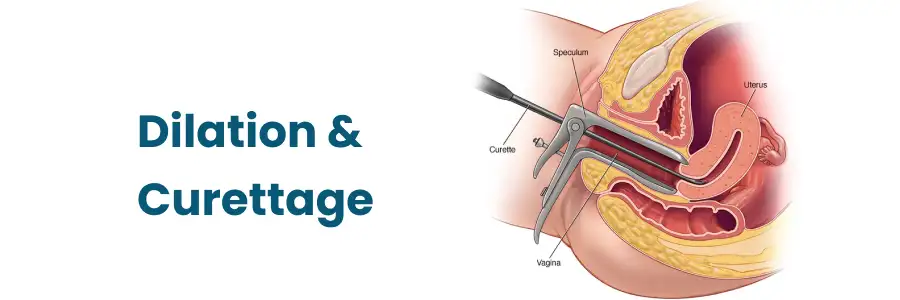
Dilation And Curettage (D & C) is a common gynecological surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat conditions involving the uterus (womb). It involves dilating the cervix (the lower, narrow part of the uterus) and scraping or suctioning the endometrial lining (the inner layer of the uterus). The procedure can be performed for diagnostic purposes - to determine the cause of abnormal uterine bleeding or to test for uterine cancer - or for therapeutic reasons, such as removing retained tissue after a miscarriage or abortion.
Historically, D&C has been one of the most frequently performed procedures in gynecology, offering both therapeutic relief and diagnostic clarity. Today, it is often complemented by or combined with modern techniques such as hysteroscopy (direct visualization of the uterine cavity) to ensure precision and safety.
A Dilation and Curettage may be recommended in several clinical situations, including:
-
Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) that cannot be explained through imaging alone.
-
Postmenopausal bleeding, which can signal hormonal imbalance or early cancerous changes.
-
Incomplete miscarriage or abortion, when tissue remains inside the uterus.
-
Suspected uterine polyps or fibroids.
-
Endometrial sampling, especially in women with prolonged heavy bleeding or infertility issues.
The procedure is generally short (15-30 minutes) and performed under local, regional, or general anesthesia, depending on the patient's condition. Most women return home the same day, making it an outpatient or day-care procedure.
Causes and Risks Related to Dilation and Curettage (D & C)
Dilation and Curettage (D&C) is a medical procedure that involves the dilation of the cervix and scraping or suctioning of tissue from the lining of the uterus. It is commonly used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Some of the main causes for performing a D&C include:
A. Common Reasons or Indications for D & C
The need for a D&C arises from a wide variety of gynecological and reproductive conditions.
-
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (AUB):
-
One of the leading reasons for performing D&C.
-
The procedure helps both stop the bleeding and obtain tissue samples for histopathological examination.
-
-
Incomplete or Missed Miscarriage:
-
Sometimes, after a miscarriage, part of the pregnancy tissue remains attached to the uterine wall.
-
This can cause infection, heavy bleeding, or pain. D&C helps clear retained products of conception (RPOC) safely.
-
-
Molar Pregnancy:
-
In cases of gestational trophoblastic disease, D&C is essential to remove abnormal trophoblastic tissue.
-
-
Postpartum Complications:
-
After childbirth, retained placenta or membranes can lead to postpartum hemorrhage (PPH). D&C helps remove these remnants.
-
-
Endometrial Polyps or Fibroids:
-
D&C assists in diagnosis and sometimes partial removal of small polyps or fibroids protruding into the uterine cavity.
-
-
Endometrial Hyperplasia or Cancer:
-
When abnormal thickening of the uterine lining is seen on ultrasound, D&C allows for biopsy and further diagnosis.
-
B. Risk Factors
Although D&C is a generally safe and commonly performed procedure, certain predisposing factors may increase the risk of complications:
-
Previous uterine surgery or scarring (e.g., multiple cesarean sections).
-
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or active infections.
-
Clotting disorders or anticoagulant medication use.
-
Postmenopausal uterine fragility, where tissues are more susceptible to injury.
-
Multiple prior D&C procedures, increasing the risk of intrauterine adhesions.
-
Structural abnormalities like bicornuate uterus or fibroids distorting the uterine cavity.
Symptoms and Signs Related to Dilation and Curettage (D & C)
Dilation and Curettage (D&C) is a procedure commonly used for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes in the female reproductive system. While D&C is generally safe, there are certain symptoms and signs that women may experience either before, during, or after the procedure. These symptoms can vary depending on the underlying condition being treated or the procedure's outcome.
Before D&C: Symptoms That Lead to the Procedure
Patients may experience one or more of the following symptoms prompting a gynecologist to recommend D&C:
-
Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia).
-
Intermenstrual spotting or bleeding between periods.
-
Bleeding after sexual intercourse.
-
Pelvic or lower abdominal pain and cramps.
-
Foul-smelling vaginal discharge, indicating possible retained tissue or infection.
-
Postmenopausal bleeding, which always warrants investigation.
-
Missed miscarriage symptoms - lack of fetal heartbeat or persistent tissue retention seen on ultrasound.
After D&C: Expected Normal Recovery Signs
After the procedure, most women experience:
-
Mild to moderate abdominal cramping for a few hours.
-
Light vaginal bleeding or spotting for 2-7 days.
-
Fatigue or weakness due to anesthesia effects.
When to Seek Medical Attention Post-D&C
Seek urgent medical help if any of the following occur:
-
Heavy bleeding (soaking more than one pad per hour).
-
High-grade fever or chills (infection sign).
-
Severe abdominal pain not relieved by medication.
-
Foul-smelling vaginal discharge.
Diagnosis and Preoperative Evaluation Before Dilation and Curettage (D & C)
Before proceeding with D&C, doctors undertake a comprehensive diagnostic and preoperative evaluation to ensure the procedure is safe and necessary.
A. Clinical Assessment
-
Detailed medical and menstrual history.
-
Physical and pelvic examination to assess uterine size, tenderness, and cervical condition.
B. Diagnostic Investigations
-
Ultrasound (Transvaginal or Pelvic):
-
Identifies fibroids, polyps, or retained tissue.
-
Evaluates endometrial thickness.
-
-
Blood Tests:
-
Complete blood count (CBC) to assess for anemia or infection.
-
Coagulation profile for bleeding risk.
-
β-hCG levels in suspected pregnancy-related conditions.
-
-
Pap Smear and Cervical Culture:
-
To rule out cervical abnormalities and infections before surgery.
-
-
Endometrial Sampling:
-
In some cases, a small tissue sample may be obtained in the clinic before proceeding with full D&C.
-
-
Pre-Anesthesia Evaluation:
-
Includes checking heart rate, blood pressure, and general fitness for anesthesia.
-
Treatment Procedure: Dilation And Curettage (D & C)
Dilation and Curettage (D&C) is a medical procedure in which the cervix is dilated, and the lining of the uterus is scraped or suctioned out using specialized instruments. This procedure is commonly used for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes in gynecological care.
A. Preparation for the Procedure
-
Fasting: Usually required 6-8 hours before surgery.
-
Medication adjustments: Blood thinners or antiplatelets may need temporary suspension.
-
Consent: The procedure, risks, and potential outcomes are explained in detail.
B. The Procedure Step-by-Step
-
Anesthesia Administration:
-
Depending on the case, local, regional, or general anesthesia is given.
-
-
Positioning:
-
The patient lies in the lithotomy position (legs supported in stirrups).
-
-
Cervical Dilation:
-
The cervix is gently dilated using Hegar dilators or other instruments.
-
-
Curettage:
-
A curette (a spoon-shaped instrument) is inserted to scrape the uterine lining.
-
In modern settings, suction curettage (vacuum aspiration) is preferred for reduced trauma.
-
-
Tissue Collection:
-
The removed tissue is sent to a pathology laboratory for microscopic analysis.
-
-
Recovery:
-
The patient is observed in the recovery area for a few hours before discharge.
-
C. Post-Procedure Care
-
Rest for 1-2 days.
-
Use sanitary pads only (no tampons or douching).
-
Avoid sexual activity for about 2 weeks.
-
Follow-up visit in 1-2 weeks to review pathology results.
Prevention and Management of Conditions Requiring D&C
Although not all cases can be prevented, good reproductive and gynecological care can reduce the need for surgical intervention.
Preventive Measures
-
Maintain regular gynecological check-ups.
-
Treat menstrual irregularities promptly.
-
Manage hormonal disorders like PCOS and thyroid imbalance.
-
Use safe contraceptive methods to avoid unwanted pregnancy and complications.
-
Promptly treat uterine or pelvic infections.
Post-D&C Management
-
Monitor recovery closely for signs of infection or complications.
-
If performed after miscarriage, psychological counseling may be helpful.
-
Discuss fertility planning with your doctor, especially after multiple D&Cs.
-
Incorporate a nutrient-rich diet with iron and vitamins to replenish blood loss.
Complications of Dilation And Curettage (D & C)
While rare, complications may occur, including:
-
Uterine Perforation:
-
Accidental puncture by surgical instruments.
-
Usually minor and self-healing, but may require observation.
-
-
Cervical Injury:
-
Small tears during dilation, usually controlled with stitches or medication.
-
-
Excessive Bleeding:
-
Rare, but possible if underlying bleeding disorder exists.
-
-
Infection:
-
Can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease if not promptly treated.
-
-
Asherman's Syndrome (Intrauterine Adhesions):
-
Scar tissue forms inside the uterus, leading to lighter periods or infertility.
-
Often managed with hysteroscopic adhesiolysis.
-
-
Anesthesia Reactions:
-
Mild allergic reactions, nausea, or dizziness can occur post-anesthesia.
-
Living with the Condition and Recovery After Dilation and Curettage (D & C)
The condition leading to a Dilation and Curettage (D&C) procedure may vary, but it often involves abnormal uterine conditions, miscarriage, or uterine infections. Living with the underlying condition before the procedure can be emotionally and physically challenging. Here's how to cope with such conditions:
Physical Recovery
Most women resume normal activities within 24-48 hours. Mild spotting and cramps are normal. Menstrual cycles usually return within 4-6 weeks.
Emotional Recovery
If the D&C followed a miscarriage, the emotional toll can be significant. Counseling and support groups can aid healing.
Sexual and Reproductive Health
-
Avoid intercourse for 2 weeks or until the doctor approves.
-
Fertility generally remains intact after D&C, but multiple procedures increase risk of uterine scarring.
Follow-Up Care
-
Attend scheduled follow-ups.
-
Review biopsy or pathology results to rule out serious underlying disease.
-
Maintain a healthy lifestyle with proper diet, hydration, and rest.
Top 10 Frequently Asked Questions about Dilation and Curettage (D & C)
1. What is Dilation and Curettage (D&C)?
Dilation and Curettage (D&C) is a medical procedure that involves the dilation (opening) of the cervix to allow the surgeon to remove tissue from the inside of the uterus. This procedure can be used for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes, such as removing abnormal tissue, diagnosing uterine conditions, or performing a pregnancy-related procedure (e.g., after a miscarriage). The procedure is usually done under general anesthesia or sedation to ensure patient comfort.
2. Why is a D&C performed?
A D&C can be performed for several reasons, including:
-
Diagnosing uterine conditions: If a patient experiences abnormal bleeding or other symptoms, a D&C may be performed to remove tissue for examination (e.g., biopsy).
-
Treatment for abnormal uterine bleeding: When bleeding is irregular or excessive, a D&C can remove the lining of the uterus to control bleeding.
-
Miscarriage management: After a miscarriage, a D&C may be done to clear any remaining tissue in the uterus.
-
Polyps or fibroids: Removal of uterine polyps or fibroids to relieve symptoms.
-
Endometrial hyperplasia: A thickening of the uterine lining, which can be treated with a D&C to prevent complications like cancer.
3. How is D&C performed?
During a D&C procedure:
-
Anesthesia: The patient is given either general anesthesia (where they are completely asleep) or local anesthesia (numbing the cervix and surrounding area).
-
Dilation of the cervix: The cervix is gently dilated (opened) to allow access to the uterus.
-
Curettage: A specialized instrument (curette) is used to gently scrape or suction the lining of the uterus to remove the tissue.
-
Recovery: After the procedure, the patient is monitored in a recovery area for a short time before being allowed to go home.
The procedure typically lasts 10 to 30 minutes, depending on the reason for the D&C.
4. Is D&C a painful procedure?
A D&C procedure is generally well-tolerated because it is performed under anesthesia or sedation. While there may be some cramping or discomfort after the procedure as the anesthesia wears off, most patients report feeling only mild pain or a sensation of heaviness in the lower abdomen. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, can be taken to manage any discomfort. If you experience severe pain or complications, it's important to contact your healthcare provider.
5. What are the risks and complications of D&C?
While D&C is generally safe, like any medical procedure, there are some potential risks and complications, including:
-
Infection: Any surgical procedure carries a risk of infection. If an infection develops, antibiotics will be prescribed.
-
Bleeding: Some bleeding or spotting is normal after the procedure, but excessive bleeding may require medical attention.
-
Perforation of the uterus: Rarely, the uterus may be accidentally punctured during the procedure, which may require further treatment.
-
Asherman's syndrome: In rare cases, excessive scarring inside the uterus can occur after a D&C, which may lead to fertility issues or future complications.
-
Emotional distress: If a D&C is performed after a miscarriage, some women may experience emotional distress or grief, which is normal. Counseling or support groups may help.
6. What should I expect during recovery after a D&C?
Recovery after a D&C is typically straightforward:
-
Post-procedure bleeding: Mild spotting or light bleeding is common and may last for a few days to 1-2 weeks.
-
Cramping: Mild cramping, similar to menstrual cramps, is normal. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help relieve discomfort.
-
Rest: It is important to rest for the first 24-48 hours after the procedure and avoid strenuous activities, including heavy lifting and exercise.
-
Follow-up appointment: Your doctor will likely schedule a follow-up visit within 1-2 weeks to ensure proper healing and address any concerns.
-
Emotional care: If the D&C was performed due to miscarriage, it's important to seek emotional support and allow time for grieving.
7. How long does it take to recover after a D&C?
Most women recover from a D&C within 1 to 2 weeks, but it depends on individual factors and the reason for the procedure.
-
Physical recovery: You may experience mild discomfort, spotting, or light bleeding for a few days to a week.
-
Resuming normal activities: You can usually return to most daily activities within a few days, but avoid heavy exercise, lifting, or sexual intercourse for at least 2 weeks to allow your body to heal properly.
If you have any complications or experience abnormal symptoms, consult your doctor for advice.
8. Can I get pregnant after a D&C?
Yes, it is possible to get pregnant after a D&C, but it is generally recommended to wait 1-3 months before trying to conceive. This allows your body to fully recover, and it gives your uterus time to heal. If the D&C was performed following a miscarriage, waiting allows the uterine lining to become thick enough to support a future pregnancy.
If you are concerned about fertility or have experienced multiple miscarriages, your doctor can guide you on the best course of action and provide advice on timing.
9. How soon can I return to work or school after a D&C?
Most women are able to return to work or school within a few days after a D&C procedure, provided there are no complications. However, it's important to listen to your body and take time to rest if needed. If you experience excessive bleeding, severe cramps, or any complications, it's advisable to take more time off to recover. Always check with your doctor about when it's appropriate to resume normal activities based on your specific situation.
10. Are there any long-term effects or side effects from D&C?
For most women, a D&C is a one-time procedure with no long-term effects. However, in rare cases, some women may experience:
-
Cervical or uterine scarring: Excessive scarring from repeated D&C procedures could lead to fertility problems or complications during future pregnancies.
-
Emotional impact: If the D&C was performed due to miscarriage or another difficult circumstance, women may experience emotional distress or depression, which may require counseling or therapy.
-
Asherman's syndrome: A rare complication where scar tissue forms inside the uterus, potentially affecting fertility. This is more likely to occur after multiple D&C procedures.
Your doctor will discuss any potential long-term risks and help ensure you receive the proper care after the procedure.