Age Spots
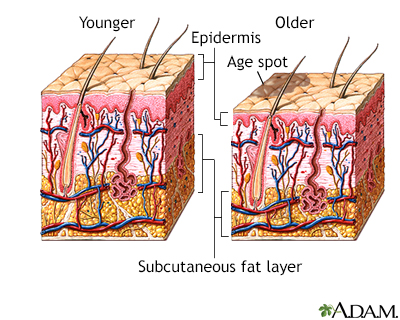
Age spots, also known as liver spots or sun spots, are flat brown, gray, or black spots that commonly appear on sun-exposed areas of the skin, such as the hands and face. While they may start developing early in life, they are most common in middle age and older adulthood, especially in individuals who spend a lot of time in the sun. Although age spots are not cancerous and do not develop into cancer, it is advisable to have a dermatologist evaluate any new spots on the skin. Factors contributing to age spots include sun exposure and genetics. Removal options are available for those who wish to diminish the appearance of age spots.
Causes of Age Spots:
- Excess Melanin Production: Age spots result from an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color.
- Hereditary Predisposition: Some individuals may have a higher likelihood of developing age spots if there is a family history of them.
- Skin Aging: Changes in pigment production and distribution associated with aging can contribute to the formation of age spots.
- UV Light Exposure: Exposure to UV light, both from the sun and tanning beds, is a significant factor in the development of age spots.
Common Areas of Development: Age spots are most likely to appear on skin areas:
- Face
- Backs of the hands
- Shoulders
- Upper back
- Forearms
Who is at the risk for age spot?
- Age: Age spots are more common in individuals older than 40 years old. The likelihood of developing age spots tends to increase with age.
- Skin Type: People with fair skin are at a higher risk of developing age spots. Fair-skinned individuals generally have less melanin, making their skin more susceptible to the effects of UV radiation.
- Sun Exposure: A history of frequent sun exposure is a significant risk factor for age spots. Prolonged exposure to UV rays from the sun can stimulate the production of melanin, leading to the formation of these spots.
- Tanning Bed Use: Individuals with a history of frequent tanning bed use are also at an increased risk of developing age spots. Tanning beds emit UV radiation, which can contribute to the development of pigmented skin lesions.
The symptoms of age spots:
- Color: Age spots exhibit a range of colors, typically from light brown to black. Exposure to sunlight can cause them to darken over time.
- Texture: Age spots have the same texture as the surrounding skin. They are flat to the touch and do not cause any pain or discomfort.
- Size: The size of age spots can vary, ranging from as small as a freckle to as large as an inch in diameter.
- Grouping: Age spots may appear individually or in groups. The clustering of spots can make them more noticeable.
- Shape: Age spots typically have round or oval shapes with well-defined edges.
How can I get rid of age spots?

1. Sunscreen: Using sunscreen is a crucial part of managing and preventing age spots, as exposure to UV radiation is a significant factor in their development.
- Broad-Spectrum Protection: Select a sunscreen that offers broad-spectrum protection, covering both UVA and UVB rays. Look for a product with a Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of at least 30.
Broad-spectrum protection is particularly important for individuals with age spots because it helps prevent further sun damage that can exacerbate existing spots or contribute to the formation of new ones.(i)Preventing Darkening (ii)Minimizing UV-Induced Aging(iii) Reducing the Risk of New Age Spots (iv)Overall Skin Health. - Water-Resistant Formula: If you’ll be swimming or sweating, choose a water-resistant sunscreen to ensure longer-lasting protection. Choosing a water-resistant formula for sunscreen is a smart choice, especially if you have age spots or are concerned about sun damage.(i)Longer Lasting Protection(ii)Maintaining Sunscreen Effectiveness(iii)Active Lifestyles.
- Apply Generously: Use an ample amount of sunscreen and reapply it every two hours, or more frequently if you are swimming or sweating. Be sure to cover all exposed skin, including the face, hands, and any other areas prone to age spots.Applying sunscreen generously is crucial when managing and preventing age spots. (i)Use Enough Product(ii) Cover Exposed Areas (iii)Don’t Forget Your Neck and Ears (iv)Apply 15 Minutes Before Sun Exposure (v)Reapply Every Two Hours (vi)Use Sunscreen Every Day (vii)Combine with Other Sun Protection Measures.
- Daily Use: Make sunscreen a daily habit, even on cloudy days or during the winter months. UV rays can penetrate clouds and cause skin damage even when the sun is not visibly strong.Using sunscreen daily is a key component of managing age spots and preventing further sun damage.(i)Consistent Application(ii)Morning Routine:(iii)Broad-Spectrum Protection(iv)Reapplication(v)Sensitive Areas:(vi)Daily Moisturizer with SPF(vii)Sun-Protective Clothing(viii)Year-Round Protection
- Choose the Right Type: Consider your skin type and preferences when choosing between lotions, creams, gels, or sprays. Some individuals with sensitive skin may prefer mineral-based sunscreens containing zinc oxide or titanium dioxide. Choosing the right type of sunscreen for age spots involves considering your skin type, preferences, and specific needs.(i)Skin Type(ii)Formulation(iii)SPF Level(iv)Broad-Spectrum Protection(v)Water Resistance(vi)Fragrance-Free Options(vii)Daily Moisturizer with SPF(viii)Consider Dermatologist Recommendations.
- Additional Protection: In addition to sunscreen, consider wearing protective clothing, such as wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and long sleeves, to further shield your skin from the sun.(i)Protective Clothing(ii)Seek Shade(iii)Use Umbrellas(iv)Avoid Tanning Beds(v)Regular Skin Checks(vi)Stay Hydrated(vii)Consider Antioxidants(viii)Gentle Cleansing(ix)Topical Treatments(x)Regular Dermatologist Visits.
- Avoid Peak Sun Hours: Try to limit your sun exposure during peak hours, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when the sun’s rays are strongest. Avoiding peak sun hours is a practical and effective strategy for managing age spots and reducing the risk of sun damage. The sun’s rays are strongest during certain hours of the day, and minimizing exposure during these times can help protect your skin.(i)Know the Peak Hours(ii)Plan Outdoor Activities Accordingly(iii)Seek Shade(iv)Wear Protective Clothing(v)Use Sunscreen(vi)Limit Sunbathing(vii)Be Mindful of Reflection(viii)Plan Outdoor Exercise.
2. Topical Treatments: Topical treatments can be effective in managing age spots, helping to lighten their appearance or prevent new ones from forming.
(i)Over-the-Counter (OTC) Products: Over-the-counter (OTC) products can be effective in managing age spots and promoting a more even skin tone.(i)Vitamin C(ii)Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs)(iii)Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHAs)(iv)Niacinamide (Vitamin B3)(v)Licorice Extract(vi)Retinol(vii)Kojic Acid(viii)Topical Antioxidants.
(ii)Prescription Medications: Prescription medications are sometimes recommended by dermatologists for the treatment of age spots, particularly when over-the-counter products are not effective.(i)Topical Retinoids (Tretinoin)(ii)Hydroquinone:(iii)Topical Corticosteroids(iv)Combination Therapies(v)Chemical Peels(vi)Laser Therapy.
3. Chemical Peels: Chemical peels are a dermatological procedure that involves the application of a chemical solution to the skin, leading to exfoliation and the eventual peeling off of the top layer of skin. Chemical peels can be effective in addressing various skin concerns, including age spots. (i)Exfoliation(ii)Stimulation of Skin Renewal(iii)Reduction of Pigmentation(iv)Types of Chemical Peels(v)Multiple Sessions.
4. Laser Therapy: Laser therapy is a medical procedure that uses focused beams of light to target specific areas of the skin.(i)Targeting Pigment(ii)Breakdown of Pigmented Cells(iii)Stimulating Collagen Production(iv)Types of Lasers:-Q-Switched Lasers;Fractional Lasers;Intense Pulsed Light (IPL)(v) Number of Sessions.
5. Cryotherapy: Cryotherapy is a medical p rocedure that involves using extreme cold to freeze and destroy abnormal tissues, including age spots.This involves freezing the age spots with liquid nitrogen, causing the darkened areas to peel off. Cryotherapy should only be done by a healthcare professional.(i)Application of Liquid Nitrogen(ii)Cell Destruction(iii)Peeling and Healing(iv)Stimulation of Skin Renewal.
6. Microdermabrasion: Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive cosmetic procedure that involves the use of a machine to exfoliate and remove the outermost layer of skin. While it’s primarily used for improving the texture and appearance of the skin, it may have some benefits for addressing age spots.(i)Exfoliation:(ii)Stimulation of Collagen Production(iii)Evening Skin Tone.

7. Natural Remedies: While natural remedies may not completely eliminate age spots, they may help lighten their appearance and contribute to overall skin health. (i)Lemon Juice(ii)Apple Cider Vinegar(iii)Aloe Vera(iv)Green Tea Extract(v)Castor Oil(vi)Papaya(vii)Turmeric(viii)Onion Extract.