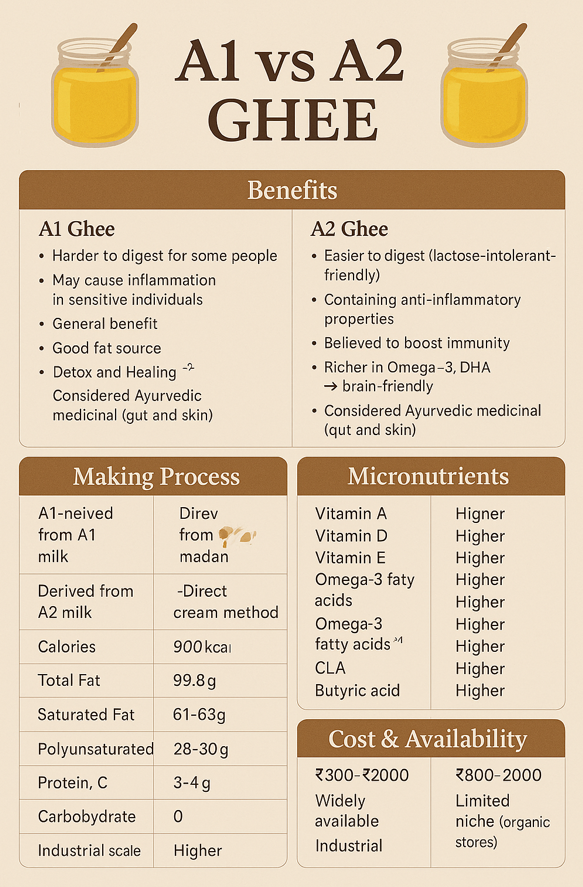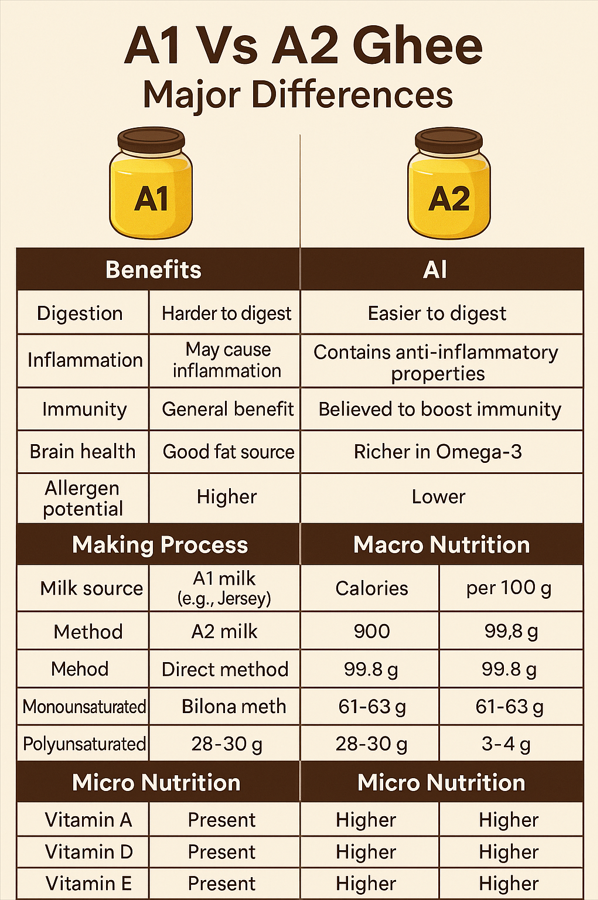
The major differences between A1 and A2 ghee—in terms of benefits, making process, and nutritional profile—stem primarily from the type of milk protein (beta-casein) in the milk used to produce the ghee. Below is a comprehensive comparison:
🧬 1. Source of Milk (Fundamental Difference)
| Feature | A1 Ghee | A2 Ghee |
|---|---|---|
| Derived from | A1 milk (from Jersey, Holstein, etc.) | A2 milk (from indigenous cows like Gir, Sahiwal, Red Sindhi) |
| Beta-casein type | A1 beta-casein | A2 beta-casein |
🌿 2. Making Process
| Process Stage | A1 Ghee | A2 Ghee |
|---|---|---|
| Milk Source | Commercial dairy farms (hybrid cows) | Desi cows (often grass-fed, free-range) |
| Method | Direct cream method or commercial heating | Traditional bilona method (cultured method) |
| Steps (Bilona) | Curd is made from milk → churned → butter → heated to make ghee | Often handcrafted, lower heat to retain nutrients |
| Heating Temperature | High heat used in industrial processing | Medium heat to preserve nutrients and aroma |
🧠 3. Health Benefits
| Criteria | A1 Ghee | A2 Ghee |
|---|---|---|
| Digestion | Harder to digest for some people | Easier to digest (lactose-intolerant-friendly) |
| Inflammation | May cause inflammation in sensitive individuals | Contains anti-inflammatory properties |
| Immunity | General benefit | Believed to boost immunity (due to CLA, Omega-3s) |
| Brain health | Good fat source | Richer in Omega-3, DHA → brain-friendly |
| Detox & Healing | Less emphasized | Considered Ayurvedic medicinal (gut and skin) |
| Allergen Potential | Higher (due to BCM-7 protein from A1 beta-casein) | Lower (A2 beta-casein doesn’t release BCM-7) |
Note: BCM-7 is a peptide released from A1 beta-casein which may be linked to some autoimmune and gut issues in susceptible individuals.
🍽️ 4. Macronutrients Comparison (per 100g)
| Nutrient | A1 Ghee | A2 Ghee |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | ~900 kcal | ~900 kcal |
| Total Fat | 99.8 g | 99.8 g |
| Saturated Fat | 61-63 g | 61-63 g |
| Monounsaturated | 28-30 g | 28-30 g |
| Polyunsaturated | 3-4 g | 3-4 g |
| Protein, Carbs | 0 | 0 |
🔬 5. Micronutrients Comparison
| Micronutrient | A1 Ghee | A2 Ghee |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A | Present | Higher bioavailability |
| Vitamin D | Present | Higher (sun-fed cows) |
| Vitamin E | Present | Higher (due to grass-fed cows) |
| Vitamin K2 | Present in small amount | Higher (supports bone health) |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Low to moderate | Higher (especially DHA) |
| Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) | Lower | Higher (anti-cancer, anti-fat) |
| Butyric acid | Present | Higher (great for gut health) |
🏷️ 6. Cost & Availability
| Criteria | A1 Ghee | A2 Ghee |
|---|---|---|
| Price per 500g | ₹300–₹600 | ₹800–₹2000 |
| Availability | Widely available | Limited, niche (organic stores) |
| Sustainability | Industrial-scale | Often sourced ethically |
✅ Summary: Which One is Better?
| Scenario | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| You want best digestibility | A2 Ghee |
| You’re lactose/gluten intolerant | A2 Ghee |
| You’re on budget | A1 Ghee |
| Ayurvedic/holistic use | A2 Ghee |
| Cooking at high temperature | Both (high smoke point) |
| Want maximum nutrition | A2 Ghee (especially bilona) |
🧪 Final Verdict:
- A2 ghee is nutritionally superior, easier on the gut, and often sourced using traditional, ethical methods.
- A1 ghee is more commercial and may suffice for everyday cooking, but might not suit sensitive individuals due to potential BCM-7 effects.