What is Cellulite?
Cellulite is a condition characterized by the appearance of lumpy, dimpled skin, typically on areas of the body with subcutaneous fat, such as the thighs, hips, and buttocks. Commonly known as “orange-peel skin,” “cottage-cheese skin,” or “hail damage,” cellulite results from fat deposits pushing against connective tissue beneath the skin, creating an uneven surface. While it can affect both men and women, it is more prevalent in females due to differences in fat distribution. Estimates suggest that between 80 to 90 percent of women may experience cellulite at some point in their lives. Despite various available treatments, including noninvasive and minimally invasive options, there is no universally effective solution, and improvements in cellulite appearance are often short-lived. Cellulite is not harmful but can lead to negative psychosocial and quality of life issues for affected individuals.
How Many Types of Cellulite?
Cellulite is not a uniform condition and can manifest in various types, each with distinct characteristics and treatment approaches.
- Soft Cellulite: Also known as flaccid cellulite, it is characterized by sagging skin and is typically found in areas where fat accumulates, such as the arms, stomach, hips, buttocks, and legs. It is more noticeable when lying down and can be improved with diet, exercise, and sometimes compression garments.
- Hard Cellulite: Often referred to as compact cellulite, it creates a “orange peel” appearance and can affect individuals regardless of their body weight or tone. Hard cellulite is characterized by firm, painful nodules and is commonly found on the thighs, buttocks, and hips. Treatment options may include excision-based procedures or other minimally invasive techniques.
- Edematous Cellulite: This type is linked to poor circulation and fluid retention, leading to swelling and a puffy appearance, especially in the lower legs. It can be challenging to treat and may require measures to improve blood circulation and reduce fluid retention, such as compression garments, hot baths, or lymphatic drainage massages.
Cellulite can be classified based on its severity using a grading scale:
- Grade 0: No visible cellulite, but structural changes may be occurring beneath the skin.
- Grade 1: Minimal visible dimpling, often described as an “orange peel” effect.
- Grade 2: More pronounced dimpling visible when standing, but may disappear when lying down.
- Grade 3: Severe cellulite with visible dimples even when lying down, often accompanied by hardness and pain.
Cellulite can also be categorized into different types based on its composition and appearance:
- Adipose Cellulite: Associated with excess fat, creating a soft, dimpled appearance.
- Aqueous Cellulite: Linked to water retention, resulting in a less pronounced dimpling pattern.
- Fibrous Cellulite: Characterized by hardened collagen fibers surrounding fat cells, leading to a rough, bumpy texture.

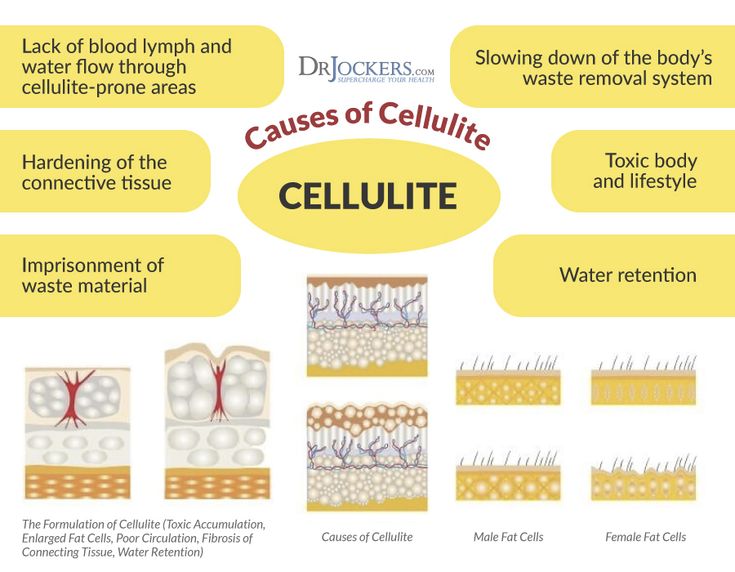
What are the Causes of Cellulite?
- Connective Tissue Structure: Fibrous bands connecting the skin to underlying muscle can tighten irregularly, pulling down on the skin while fat pushes upward, leading to a puckering appearance.
- Hormonal Influence: Hormones like estrogen, insulin, thyroid hormones, and prolactin may contribute to cellulite development. Changes in estrogen levels, such as during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, can impact blood flow, collagen production, and fat accumulation.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic variations can influence metabolism, fat distribution, and skin structure, all of which may contribute to the likelihood of developing cellulite. Family history can be a significant predictor of cellulite risk.
- Diet and Lifestyle: While cellulite is not directly caused by toxins, poor dietary habits, including excessive consumption of fat, carbohydrates, and salt, and insufficient fiber intake, may increase the risk of cellulite. Sedentary lifestyle habits, smoking, and wearing tight clothing may also exacerbate cellulite.
- Age: Aging leads to changes in skin elasticity, thickness, and muscle tone, which can contribute to the development of cellulite. Collagen production decreases, and the skin becomes less firm, making cellulite more visible.
What are the Symptoms of Cellulite?
- Dimpled or Bumpy Skin: The primary symptom of cellulite is the presence of dimples or lumps on the skin, particularly noticeable when standing or sitting in certain positions.
- Skin Discoloration: The affected areas may exhibit a slightly different color compared to the surrounding skin. This can vary depending on individual skin tone and severity of cellulite.
- Skin Sensitivity: Some individuals may experience tenderness or sensitivity to the touch in areas affected by cellulite. This sensitivity can vary in intensity.
- Gradual Progression: Cellulite tends to develop gradually over time and may worsen if left untreated. As such, early intervention and management strategies may help mitigate its progression and appearance.
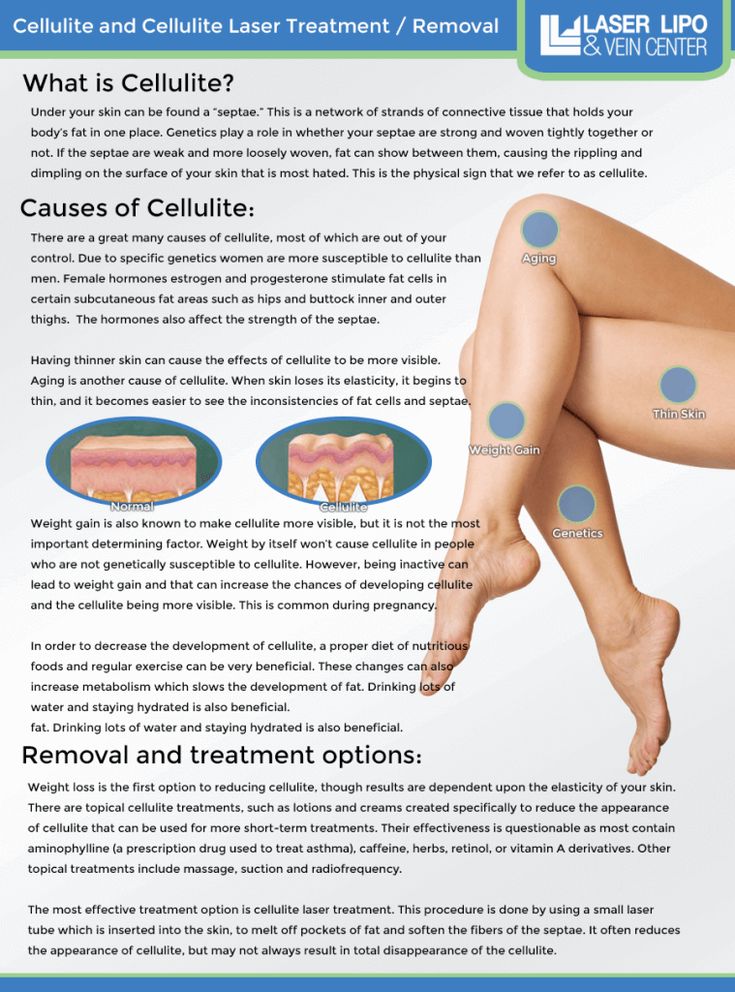
How Can I Prevent/ Reduce your risk of developing cellulite?
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Avoid processed foods that are high in carbohydrates, fats, preservatives, and salt. Instead, focus on consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Limit your intake of sugary and fatty foods, which may contribute to cellulite formation.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your skin hydrated and improve overall skin health. Proper hydration can also help prevent fluid retention, which may exacerbate the appearance of cellulite.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to improve circulation and tone muscles in areas prone to cellulite, such as the buttocks, thighs, hips, and arms. Cardiovascular exercises, strength training, and targeted exercises for problem areas can all be beneficial.
- Supplements: Consider taking supplements that contain caffeine, grape-seed extract, or ginkgo biloba, as these ingredients may help improve circulation and reduce the appearance of cellulite. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements.
- Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol: Smoking and heavy alcohol consumption can negatively impact skin health and circulation, potentially worsening the appearance of cellulite. Quit smoking and limit alcohol intake to reduce your risk.
- Protect Your Skin: Take precautions to prevent skin injuries, such as wearing sunscreen, avoiding scratching or picking at the skin, and using protective gear during physical activities or when handling hazardous materials.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being overweight or obese can increase the likelihood of cellulite formation. Aim to maintain a healthy weight through a combination of diet and exercise to reduce your risk.
- Skin Care: Keep your skin moisturized and well-nourished with regular skincare routines. Dry skin can exacerbate the appearance of cellulite, so using moisturizers and body oils can help improve skin texture and elasticity.
What are the Treatment of cellulite?
Professional Treatments:
- Pressotherapy: A controlled compression system that aids in detoxification and lymphatic drainage.
- Acoustic Wave Therapy: Uses shock waves to break down fatty deposits and improve circulation.
- Mesotherapy: Involves injecting a combination of vitamins, minerals, and hyaluronic acid into the skin to improve texture.
- Radiofrequency: Delivers energy into the dermis to tighten tissues and stimulate collagen production.
- Fat Dissolving Injections: Involves injecting a solution to dissolve fat cells.
- Cryolipolysis: Freezes fat cells, causing them to rupture and be expelled by the body.
- Laser Treatments: Procedures like Cellulaze use laser energy to release fibrous bands and liquefy fat.
- Subcision: Involves releasing constrictive fibrous bands under the skin to improve the appearance of dimples.
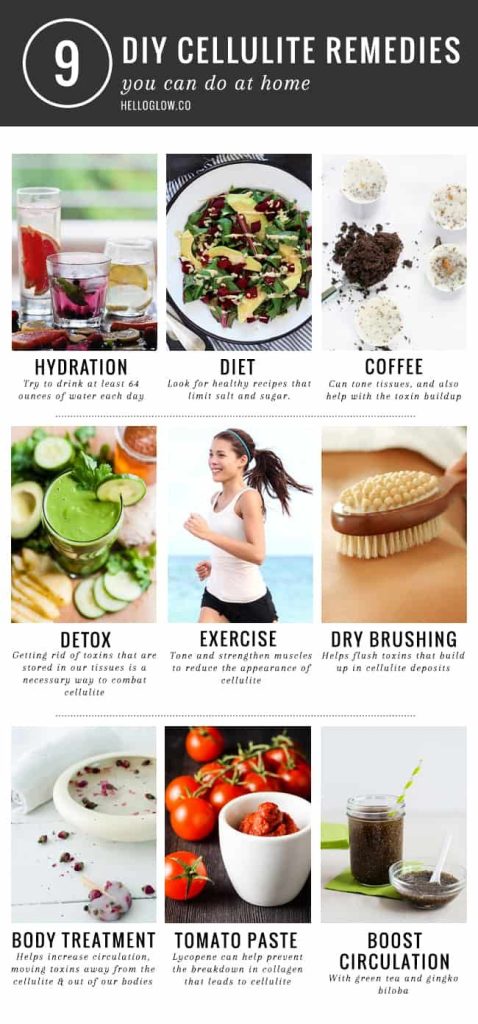
Home Remedies:
- Dry Brushing: Stimulates blood circulation and exfoliates the skin.
- Herbal Oils: Massaging with oils like sesame or coconut combined with essential oils can enhance skin elasticity.
- Triphala and Guggul: Ayurvedic supplements that aid digestion and reduce inflammation.
- Self-Massage: Regular self-massage using Ayurvedic oils promotes relaxation and skin health.
- Herbal Teas: Drinking teas made from ginger, fennel, or fenugreek aids digestion and detoxification.
- Lymphatic Massage: Professional massages improve lymphatic circulation and reduce fluid retention.
- Hydration: Proper hydration supports healthy skin and digestion.
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps reduce body fat and improve muscle tone.
- Proper Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains supports skin health.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the visibility of cellulite.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking accelerates skin aging and collagen breakdown.
- Collagen Supplementation: Supplements or foods rich in collagen can support skin elasticity and health.
Topical Treatments:
- Caffeine-based Creams: Increase blood flow and temporarily reduce the appearance of cellulite.
- Retinol Creams: Help thicken the outer layer of skin and improve texture over time.
- Other Ingredients: Various ingredients like grape seed extract and gingko biloba are used in cellulite creams, but their efficacy is still debated.

How Can I Get Rid of Cellulite?
- Stimulate the Lymphatic System: Regularly massage the affected areas using a body brush or scrub to stimulate blood and lymphatic drainage. This can help reduce the appearance of cellulite over time.
- Healthy Diet: Incorporate plenty of green, leafy vegetables into your diet while avoiding processed foods and excessive alcohol consumption. A nutritious diet can contribute to overall skin health and may help reduce cellulite visibility.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: While cellulite can affect individuals regardless of weight, maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help improve muscle mass and skin quality, thereby reducing the appearance of cellulite.
- Professional Treatments: Consult a healthcare professional or dermatologist for advanced treatments to target cellulite. FDA-approved devices like Avéli, which cuts the bands causing cellulite, can offer long-term results. Laser treatments and injectable fillers may also be effective in smoothing out the skin and improving appearance.
- Combination Therapy: Dermatologists may recommend a combination of treatments tailored to your specific needs, such as using lasers alongside injectable fillers, to achieve optimal results.