Dermatology diseases affect the skin, hair, nails, and mucous membranes. They can vary in severity from minor irritations to serious conditions such as skin cancer, and often, they significantly impact a person’s appearance, mental health, and quality of life. Whether you’re dealing with acne, psoriasis, eczema, or more severe conditions like melanoma, understanding the symptoms, causes, and available treatments is essential for effectively managing these disorders.
This guide is designed to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of common dermatological diseases, including their symptoms, causes, treatment options, and surgical procedures. Additionally, we will cover how connecting with resources like MyHospitalNow and the Dermatology Diseases Forum can offer support, expert advice, and a sense of community.
Explore MyHospitalNow for more information on dermatology diseases
Symptoms of Dermatology Diseases
Symptoms of dermatological diseases can range from mild and temporary irritation to more serious, chronic conditions. Recognizing these symptoms early can help with timely diagnosis and management.
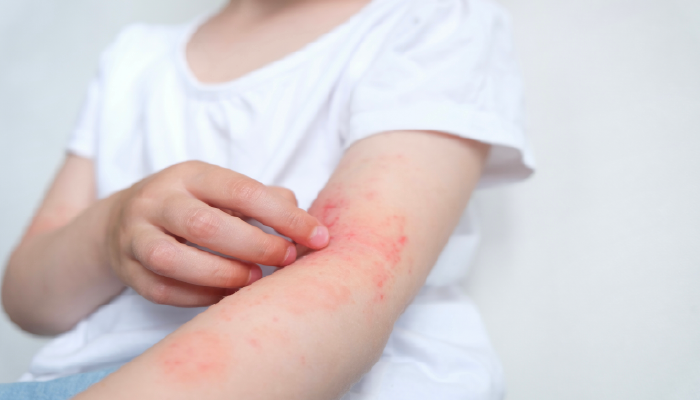
1. Skin Rashes and Redness
Rashes are a common symptom in many dermatology diseases and can range from mild irritation to serious, inflamed areas of skin.
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): Characterized by itchy, red, and inflamed skin, eczema often appears in areas like the face, hands, or behind the knees. It may be triggered by allergens, irritants, or stress.
- Psoriasis: A chronic autoimmune condition that causes the skin to produce cells too rapidly, resulting in red, scaly patches that are often itchy and uncomfortable. It commonly affects the elbows, knees, and scalp.
- Contact Dermatitis: This occurs when the skin reacts to an allergen or irritant, such as a particular type of soap, plant, or metal. Symptoms include redness, swelling, and itching.
2. Dryness and Itching
Many dermatological conditions are characterized by skin dryness and itching.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: This condition causes flaky, greasy patches on the skin, often on the scalp, face, or upper chest. It is commonly associated with itching and redness.
- Dry Skin (Xerosis): Caused by environmental factors, such as low humidity or harsh soaps, dry skin can lead to cracking, flaking, and irritation.
- Allergic Reactions: Skin reactions from allergens can lead to intense itching, hives, or even blistering.
3. Hair Loss
Hair loss or thinning can result from a variety of dermatological conditions.
- Alopecia Areata: A condition where the immune system attacks the hair follicles, causing patchy hair loss on the scalp or other parts of the body.
- Androgenetic Alopecia: Commonly referred to as male-pattern or female-pattern baldness, this genetic condition leads to gradual hair thinning.
- Fungal Infections: Conditions like tinea capitis (ringworm of the scalp) can lead to hair loss and scalp inflammation.
4. Nail Abnormalities
Changes in the nails, such as discoloration, deformities, or thickening, can be signs of dermatological disease.
- Fungal Nail Infections: This common infection causes thick, discolored nails that can be brittle and painful.
- Psoriasis: Psoriasis can also affect the nails, causing pitting (small dents in the nail), discoloration, and separation from the nail bed.
- Onycholysis: The detachment of the nail from the nail bed, often seen in conditions like psoriasis and fungal infections.
5. Skin Lesions and Growths
Skin growths, such as moles, lumps, or ulcers, can be an indication of a dermatological issue.
- Skin Cancer: Unusual growths or changes in moles (such as asymmetry, irregular borders, or changes in color) may indicate melanoma or other forms of skin cancer.
- Warts: Caused by human papillomavirus (HPV), warts are non-cancerous growths that often appear on the hands or feet.
- Basal Cell Carcinoma: A type of skin cancer that typically appears as a small, shiny bump or growth, usually on sun-exposed areas.
Causes of Dermatology Diseases
Dermatological diseases can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetic predisposition, environmental factors, infections, and lifestyle choices. Understanding the cause of your condition is crucial for effective treatment.
1. Genetic Factors
Many skin conditions are inherited, meaning they run in families and are caused by specific genetic mutations.
- Psoriasis: A hereditary autoimmune condition, psoriasis often runs in families. It causes skin cells to grow rapidly, leading to thick, red patches covered in silvery scales.
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): This common condition often affects children and may be linked to a family history of other allergic diseases like asthma or hay fever.
- Albinism: A genetic condition where there is little or no pigmentation in the skin, hair, and eyes, leading to an increased risk of sunburn and skin cancer.
2. Environmental Factors
The environment plays a significant role in the development or exacerbation of many skin diseases.
- Sun Exposure: Overexposure to UV radiation from the sun is a major cause of skin cancer, including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma.
- Climate: Extreme weather conditions, such as hot, dry air or high humidity, can contribute to dry skin, eczema, and other skin irritations.
- Pollution: Environmental pollutants like smoke, chemicals, and dust can irritate the skin and lead to conditions like eczema, rosacea, and acne.
3. Infections
Infections are a common cause of many skin diseases and can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites.
- Bacterial Infections: Impetigo (caused by staphylococcus or streptococcus bacteria) and cellulitis are common bacterial skin infections.
- Viral Infections: Herpes simplex virus (HSV) causes cold sores, while human papillomavirus (HPV) can lead to warts.
- Fungal Infections: Ringworm, athlete’s foot, and yeast infections are caused by fungi that infect the skin, hair, and nails.
- Parasites: Conditions like scabies and lice are caused by parasitic infestations.
4. Lifestyle and Habits
Certain lifestyle choices can contribute to the development or worsening of dermatological diseases.
- Diet: A poor diet high in processed foods and sugars can exacerbate conditions like acne, rosacea, and eczema.
- Smoking: Smoking accelerates the aging process of the skin and increases the risk of wrinkles, skin cancer, and poor wound healing.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol can contribute to rosacea and worsen skin conditions due to dehydration and its effects on the skin’s immune function.
5. Autoimmune and Chronic Conditions
Autoimmune diseases occur when the body’s immune system attacks healthy tissues, and many dermatological diseases are autoimmune in nature.
- Lupus: An autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation and damage to the skin, often presenting as a butterfly-shaped rash across the nose and cheeks.
- Vitiligo: An autoimmune condition that causes the skin to lose its pigment, leading to white patches on various parts of the body.
- Alopecia Areata: A condition where the immune system attacks hair follicles, leading to patchy hair loss.
Treatment Options for Dermatology Diseases
The treatment for dermatological diseases varies depending on the specific condition, severity, and individual factors. Options range from topical treatments and oral medications to advanced therapies and surgical interventions.
1. Topical Treatments
- Corticosteroids: Topical steroids are commonly prescribed for inflammatory skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis to reduce swelling, redness, and irritation.
- Topical Retinoids: Used to treat conditions like acne and psoriasis, retinoids help speed up cell turnover and reduce inflammation.
- Antifungal Creams: For fungal infections like ringworm and athlete’s foot, antifungal creams like clotrimazole and terbinafine are effective in killing the fungus.
- Emollients: Moisturizers and emollients help treat dry skin and are essential in managing conditions like eczema and seborrheic dermatitis.
2. Oral Medications
- Antibiotics: For bacterial infections like cellulitis or impetigo, oral antibiotics like amoxicillin or cephalexin may be necessary.
- Antihistamines: For itching caused by allergic reactions or hives, antihistamines like loratadine or cetirizine can provide relief.
- Systemic Steroids: For more severe conditions like psoriasis or lupus, systemic steroids are used to control inflammation and immune responses.
3. Phototherapy
- Ultraviolet (UV) Therapy: Phototherapy uses controlled exposure to UV light to treat conditions like psoriasis, eczema, and vitiligo. It helps reduce inflammation and slow down cell turnover in the skin.
4. Surgical Treatments
- Cryotherapy: This involves freezing off warts, moles, or precancerous lesions using liquid nitrogen. It’s also used to treat actinic keratosis and basal cell carcinoma.
- Excision: Surgical removal of tumors, skin cancers, or abnormal growths is often required for melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma.
- Laser Therapy: Lasers can be used to treat acne scars, age spots, spider veins, and wrinkles. They can also help remove tattoos or birthmarks.
- Skin Grafting: For extensive skin damage due to burns or other injuries, skin grafting can help restore lost skin by taking tissue from another part of the body.
Prevention and Lifestyle Modifications
While not all dermatological diseases can be prevented, there are key practices to promote healthy skin:
- Sun Protection: Always apply sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher to protect against UV radiation. This helps prevent skin cancer, sunburn, and premature aging.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins (especially vitamin C, vitamin E, and vitamin A) to promote skin health and repair.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep the skin hydrated and maintain its natural moisture.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking accelerates skin aging and increases the risk of skin cancer. Quitting helps improve skin elasticity and reduce wrinkles.
- Regular Skin Checkups: Perform self-examinations for unusual moles or growths and schedule routine visits to a dermatologist.
Support and Community in Dermatology Disease Management
Dealing with a dermatological condition can be emotionally challenging, especially if it affects your appearance. Engaging with others facing similar challenges can provide comfort and guidance. The Dermatology Diseases Forum on MyHospitalNow is a great place to find support, share experiences, and connect with others.
Join the Dermatology Diseases Forum for advice, support, and expert insights
Empowering Your Dermatology Health Journey
Dermatological diseases can be distressing, but with the right knowledge and care, many individuals can effectively manage their condition and maintain healthy, vibrant skin. Whether you’re dealing with acne, psoriasis, or more serious issues like skin cancer, early intervention and treatment are crucial.
By utilizing resources like MyHospitalNow and engaging with the Dermatology Diseases Forum, individuals can access the support, information, and expert guidance they need to navigate their dermatology health journey.
Visit MyHospitalNow for more information on dermatology diseases
Call to Action
If you’re experiencing symptoms of a dermatological disease, don’t wait to seek professional advice. Join the Dermatology Diseases Forum today to gain expert guidance, connect with others facing similar challenges, and take control of your skin health.